Clean50 2025 Clean Tech Nominee Features – Part 2/5: Mining and Materials + Research and Development

Last week, we kicked off a new series showcasing some of the most innovative startups from Canada’s cleantech sector and their cutting-edge solutions for sustainable development. The Clean50 Awards, to be announced October 10th, will capture only a fraction of the remarkable companies we’ve encountered – this is why we invite you to follow along as we amplify the best of what we’ve seen.
This series is more than just a spotlight on innovation; it’s a call to action. Our cleantech sector is paving new pathways toward sustainability and unlocking pivotal opportunities for our economy, but innovation alone isn’t enough. To reach their potential, our startups need support at all stages of development.
This week, we’re exploring the pathways and processes that turn ideas into impacts. The companies we’re featuring range from innovative concepts in development to proven technologies making waves in the market, highlighting how important it is for us to support Canada’s research and development (R&D) ecosystem. These technologies include three game-changing innovations for mining and material production that are nearing market readiness or have already hit the market in Canada, and five R&D technologies giving us a glimpse of the next generation of Canadian cleantech.
Canadian universities are core contributors to our R&D ecosystem. In labs across the country, researchers are developing the next generation of climate breakthroughs, made possible with support from institutional and industry partners. Major academic hubs for cleantech research include McGill, known for their leadership in circular economy technologies and home to the Trottier Institute for Sustainability in Engineering and Design; UBC, recognized for renewable energy advancements, housing the Clean Energy Research Centre and the BioProducts Institute; and UofT, known for spearheading AI-powered climate solutions, and for collaborating with the MaRS Discovery District on early-stage ventures. These researchers are the backbone of Canadian R&D, but they can’t do it alone. We must incentivize innovation in these academic spaces and provide the resources and support needed to foster and scale new technology.
As we introduce this week’s standout companies and projects — all representing different technology readiness levels — we invite you to join us in celebrating their work and amplifying the importance of investments and partnerships for early-stage cleantech. By enabling R&D, we’re not just driving innovation—we’re setting the stage for the investments, upskilling, partnerships, and collaboration needed for transformative climate action.
.
Profiles 1-3: Mining and Materials
.

BQE Water, David Kratochvil (President & CEO)

Company and product snapshot: BQE Water is a water treatment company that specializes in providing innovative wastewater treatment solutions to the global mining industry. One of their solutions focuses on selenium removal, which is often found in coal mining, base/precious metals, even uranium mining – any hard rock mining has the potential to produce selenium as a contaminant. BQE’s Selen-IX technology offers mining and industrial clients a sustainable, zero-waste solution that turns a harmful contaminant into a usable resource while safeguarding the environment. Their technology selectively removes that selenium, which can then be used in the steel making industry, creating zero waste. Selen-IX was born because of obvious inefficiency and dangers in existing solutions, and the impact of not continuously storing contaminated waters is in itself a massive environmental benefit to all of us.
Who should buy it: Mining companies wishing to or needing to discharge water into the environment. Also now being recognized in other industrial sectors besides mining, for example BQE Water recently built a plant for a Power Utility in the southeastern US.
.

Destiny Copper Inc., Greg Hanna (Founder & CEO)

Company and product snapshot: Destiny Copper has developed an innovative, low-cost, modular, cleantech hydro-metallurgical Copper extraction system – a breakthrough technology that could change the way copper is produced globally. The patented chemical process requires almost zero energy to produce high-purity copper powder (>99.9%) from copper-rich waste streams, such as mine tailings and industrial effluents. The ground-breaking clean technology significantly outperforms traditional copper extraction methods, such as solvent extraction electro-winning (SX-EW) and smelting, reducing CO2 emissions by up to 89%. The process provides a viable method for recovering copper from the 2.4 trillion dollars of copper that is locked away in waste and stranded resources.
Who should buy it: Green technologies such as EVs, advanced manufacturing (additive manufacturing, press-sintered parts, and injection moulding), wind turbines, and catalysts demand ever increasing amounts of copper and copper powder.
.

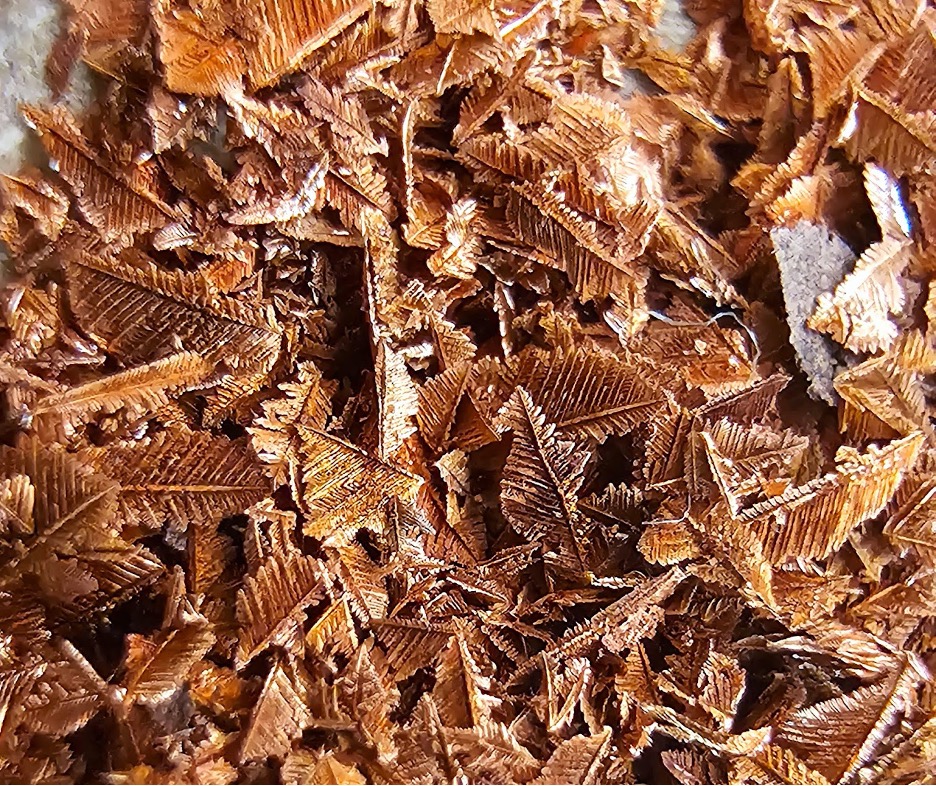
Progressive Planet Solutions, Stephen Harpur (CEO)

Company and product snapshot: Progressive Planet Solutions is a cleantech and manufacturing company based in Kamloops, British Columbia, with expertise lying in developing low-carbon and carbon sequestering solutions using mineral assets and recycled materials to create planet-friendly products. Globally, cement production accounts for 8% of CO2 emissions. Progressive Planet Solutions’ PozGlass™ 100G supplementary cementing material replaces up to 50% of Portland cement, dramatically reducing its carbon footprint without compromising performance – PozGlass has also proven to be 4-13% stronger. PozGlass uses glass diverted from landfills, decreasing the use of Portland cement and fly ash, which off gas high quantities of CO2 during production. An output of its patent-pending process is limestone, permanently sequestering CO2 from cement kiln stack gasses. Cement kilns are the third largest global producer of greenhouse gas emissions. PozGlass will eventually replace Portland cement on an equivalent, one-for-one weight basis, at one-third of the production footprint. Currently at TRL level 5, PozGlass is anticipated to be market ready in 2028. Progressive Planet Solutions has a 10-year agreement for one of the largest cement companies in the world to test PozGlass in amounts of up to 3,500 tonnes per year as soon as the pilot plant is built and commissioned to produce these quantities.
Who should buy it: Construction companies, concrete and cement manufacturers, and infrastructure developers. PozGlass replaces ready-mix or precast concrete.
.
Profiles 4-8: Research and Development
.

Carbonova Corp, Mina Zarabian (Co-founder & CEO)
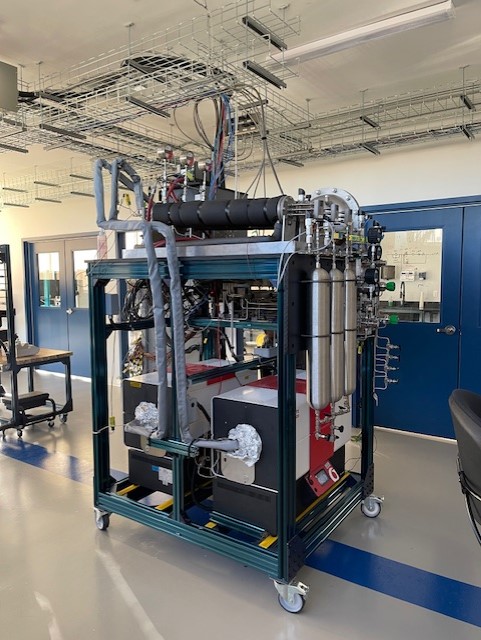

Company and product snapshot: Traditional solid carbon materials, essential in everyday products, are typically derived from fossil fuels or natural minerals, resulting in significant carbon footprints. Carbonova has pioneered a method to produce high-quality solid carbon from greenhouse CO2 and Methane gas emissions—gases that would otherwise exacerbate climate change. Carbonova’s advanced carbon nanofibers offer exceptional mechanical, thermal, electrical, and chemical properties, making them ideal for a wide range of industries, including transportation, concrete, electronics, textiles, inks, coatings, lubricants, tires, and agriculture. By leveraging this innovative carbon utilization process, Carbonova is driving environmental sustainability by (1) eliminating the need for natural resources in solid carbon nanomaterial production, and (2) transforming millions of tons of greenhouse gases into valuable products.
Who will be able to use it: Carbonova’s solution is designed for customers committed to enhancing the sustainability of their manufacturing and product components. This includes companies focused on achieving carbon neutrality, as well as advanced manufacturers in electronics, composite materials, and construction.
Market readiness: Carbonova is on course to establish the first large-scale commercial carbon nanofibers production facility in Canada, with a projected market launch in late 2026.
.

Lite-1 Bio, Roya Aghighi (CEO & Co-Founder)
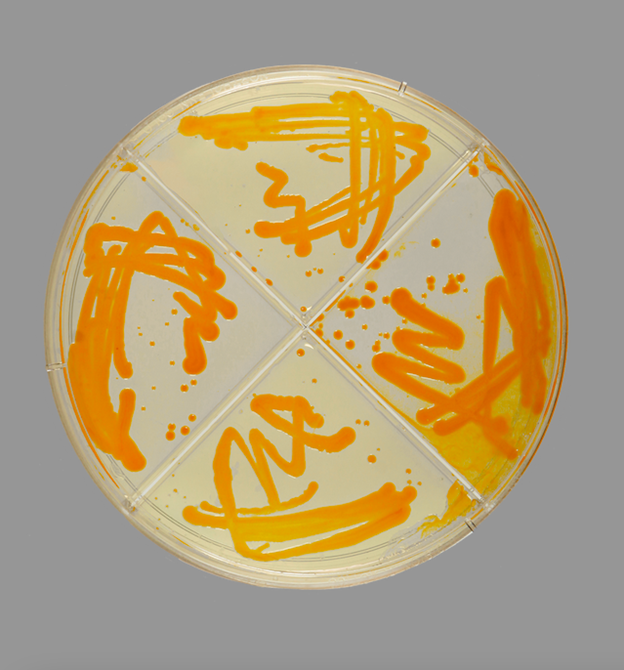
Company and product snapshot: On a global environmental scale, the dye and pigment industry is identified as one of the biggest polluting and toxic industries. Headquartered in Vancouver, Lite-1 Bio aims to transform the colour industry by introducing the next generation of 100% sustainable dyes and colourants that are high-performance and cost-competitive to conventional toxic dyes. Lite-1’s technology addresses the growing demand for clean, scalable, and cost-effective alternatives to synthetic dyes. Lite-1’s approach, currently at technology readiness level (TRL) 5, utilizes genetically engineered, non-toxic microbes to produce biodegradable dyes with less water and no toxic wastewater. Lite-1’s microbial pigments are derived from advanced biotechnological processes, where they harness microbes’ capabilities to create vibrant and consistent colours, offering a stark contrast to traditional dyes that rely heavily on petrochemical-based ingredients. This method eliminates the need for hazardous chemicals, drastically reducing synthetic dyes’ negative environmental and health impacts.
Who should buy it: Lite-1’s biotechnological platform empowers manufacturers and brands across diverse industries to create bespoke colour solutions tailored to their needs. This innovation spans a wide range of sectors, including textiles, food, cosmetics, and inks.
Market readiness: Once commercialized in Q3, 2026, Lite-1’s technology will also improve energy efficiency, reduce waste, conserve water, and provide a solution for companies that need to meet evolving government rules, regulations, and bans on the use and sale of products containing toxic dyes.
.

Developing hybrid small molecule semiconductors at the University of Toronto, Nina-Francesca Farac (Doctoral Researcher)
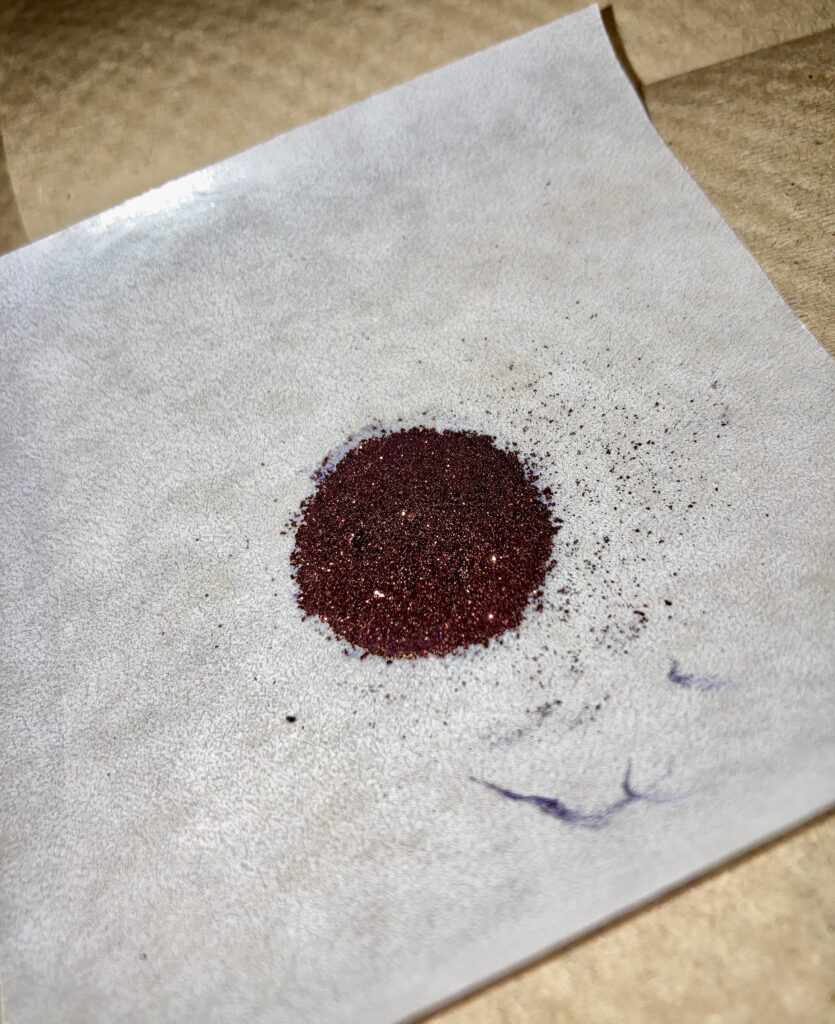

Product snapshot: In the University of Toronto’s Department of Chemical Engineering & Applied Chemistry, Doctoral Researcher Nina-Francesca Farac and her team are advancing clean energy technologies with green chemistry. Working within the Bender laboratory, Nina is developing hybrid small molecule semiconductors that will offer a 2-in-1 solution, absorbing a broad range of light for energy harvesting and emitting pure red light for lighting applications. In solar cells, they can capture more solar energy, enhancing power generation. In OLEDs, they produce vibrant, high-contrast red light, ideal for enhancing colour quality. Their dual capability could significantly boost solar panel efficiency by capturing more sunlight per surface area of panel, contributing to higher renewable energy production and reduced greenhouse gas emissions. When integrated into OLEDs, they can enable energy-efficient displays and lighting that decrease power consumption, extend the lifetime of electronic devices, and reduce the environmental footprint of consumer electronics.
Who will be able to use it: Solar energy companies, OLED display producers, electronics manufacturers, and lighting technology companies.
Market readiness: 12-15 years for solar cell applications and 10-13 years for OLED applications.
.

International Renewable Energy Systems Inc., Christopher Chukwunta (CEO)
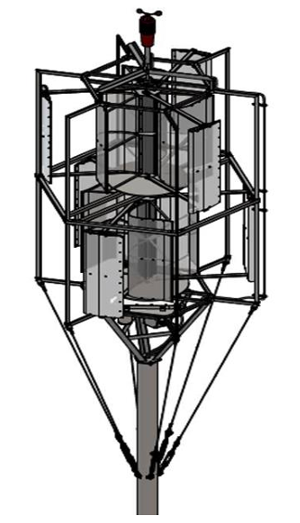
Company and product snapshot: Based in Edmonton and Warburg Alberta, IRES operates three value streams as part of their vision to transition a million homes, businesses and communities to clean energy by 2050; renewable energy solutions, clean technology, and net zero energy. Under the clean technology value stream, IRES is developing the IRES Windmine; a Vertical Axis Wind Turbine (VAWT) designed to bring the benefits of wind energy to Albertans and northern communities in an economically viable manner. The IRES Windmine taps into the complementary nature of solar and wind energy. During the day, Albertans and northern communities have lots of sun but not as much wind, and more wind but no sun at night. In the winter months, they have more wind but not so much sunlight due to shorter days and snow cover. Combining solar and wind technologies has the potential to improve power generation by up to 30% additional for the same capacity of install. The IRES Windmine has the flexibility to be used within urban and in rural locations – unlike regular wind turbines, it does not kill birds and it operates within acceptable noise levels. The IRES Windmine has a best-case scenario of up to 20,000 tonnes of CO2 equivalent emissions reduction from the first phase of product commercialization.
Who will be able to use it: IRES Windmine VAWT can be used by remote facilities like oil and gas stations (for manifolds, block valves, cathodic protection etc.), telecommunications, weather stations etc.
Market readiness: expected by Q4 2025.
.

Electro Carbon, Martin Larocque (Co-founder & CEO)
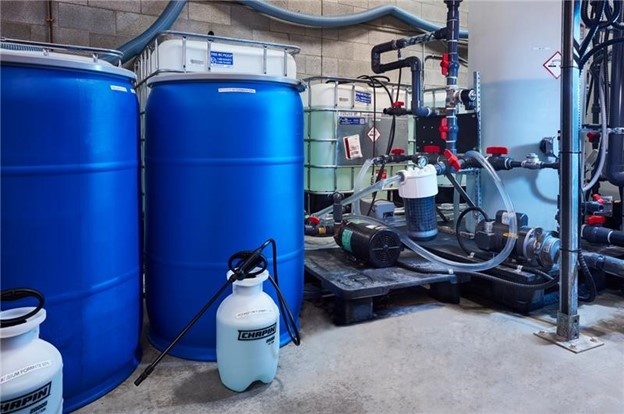

Company and product snapshot: Electro Carbon Inc., established in 2019, is a Canadian company specializing in converting CO2 into high-value specialty chemicals. The company utilizes a unique electrochemical process to produce potassium formate (HCOOK) from CO2, which is used across various industries as a de-icing material, a fertilizer, and a heat-transfer fluid, among other uses. Electro Carbon’s technology offers a sustainable substitute for conventionally produced potassium formate, which heavily relies on fossil fuels and is primarily imported from Asia and the Middle East. Electro Carbon has successfully developed and operates the world’s largest industrial CO2 electrolyzer, the ECO100, with a production capacity of 100 metric tonnes of potassium formate annually, a stepping stone that will lead to the deployment of larger scale CO2 electrolyzers in the coming years. Their innovative technology boasts a 2.15-tonne net reduction in CO2 for every tonne of potassium formate produced, significantly contributing to global decarbonization efforts. Electro Carbon’s technology presents a compelling solution to decarbonize the production of potassium formate, offering a cleaner, more sustainable, and economically viable alternative to traditional methods. An LCA (Life Cycle Analysis) performed for the Federal Government concluded that Electro Carbon’s de-icing material could be delivered in Canada with only one third the usual GHG emissions of the current solutions.
Who should buy it: While Electro Carbon’s chloride free, non-corrosive and environmentally friendly molecule will serve the highly regulated airport de-icing material for airport runways market, the company is also aiming to replace other existing harmful de-icing material (including rock salts) for bridges, ports and roads – including the front porch of your house. Other industrial applications would include the use of potassium formate as a heat transfer fluid (such as geothermal applications) and/or as a chloride-free potassium fertilizer.
Market readiness: Electro Carbon is getting ready to ship the 1st few metric tons of the “Blend” molecule by the end of 2024 and ramping up production for 2025 and beyond.