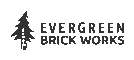Defossilization: The Case for Bio-Based Materials in Industry
Jason Robinson, Founder and CEO at Evoco Ltd., discusses how the global transition towards bio-based materials offers reduced environmental impact, high performance, biodegradability, cost efficiency, and fosters innovation. Collective commitment is crucial to accelerate this change, creating a more sustainable future by divesting from fossil fuel-dependent practices.
In response to growing environmental concerns, industries globally are pivoting towards defossilization and the adoption of bio-based materials to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and enhance sustainability. These materials offer a compelling alternative, providing high performance, biodegradability, and cost efficiency while fostering innovation and diversification across sectors. Embracing bio-based materials is not only a strategic business decision but also a necessary step towards mitigating climate change and shaping a more sustainable future, necessitating collective commitment from stakeholders to drive meaningful change.
Introduction
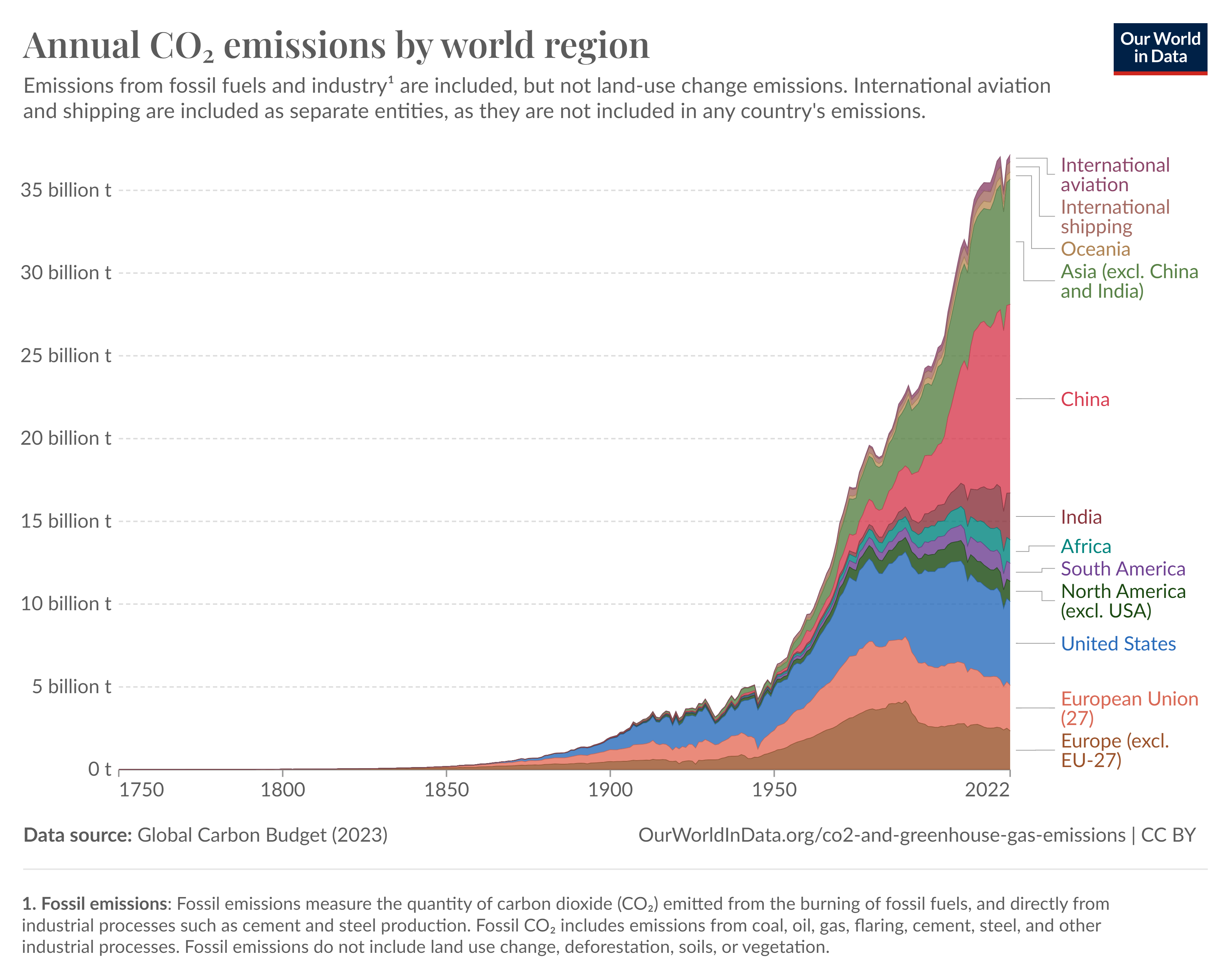
Petrochemicals are everywhere. From fashion, to furniture, to the cars we drive, producing these products results in billions of tonnes of carbon emissions – contributing to climate change. By defossilizing the supply chain and replacing oil-based raw materials with plant-based alternatives, brands can reach globally agreed and targeted ESG goals to improve their triple bottom line.
In an era marked by heightened environmental consciousness, industries worldwide are reevaluating their practices to minimize their carbon footprint and contribute to a more sustainable future. One significant avenue gaining traction is the adoption of bio-based materials and the process of defossilization. This shift not only aligns with environmental goals but also offers numerous benefits for companies across various sectors.
There are 5 Key Benefits of Defossilization of the Material Value Chain
1. Reduced Environmental Impact
The frightening consequences of climate change are global and the successful transition toward a more sustainable future is possible if we can collectively reduce the annual global CO₂e emissions across all emitting industries. We’re far too reliant on petrochemistry and fossil fuels for so many products in life and in fighting Climate Change, we need a materials transformation moving towards bio-products instead of oil products.
By transitioning to bio-based materials, companies can significantly reduce their greenhouse gas emissions, a crucial step in combating climate change. Unlike traditional petroleum-derived materials, bio-based alternatives offer a more sustainable alternative, contributing to a cleaner and healthier environment.
2. Enhanced Performance
Biomaterials maintain excellent performance attributes, ensuring that brands don’t have to compromise on quality or functionality. Contrary to misconceptions, bio-based materials are not just eco-friendly; they also offer high performance. These materials can match or even surpass the quality and functionality of their fossil fuel-derived counterparts, ensuring that companies don’t have to compromise on performance while pursuing sustainability.
“Contrary to misconceptions, bio-based materials are not just eco-friendly; they also offer high performance”
Jason Robinson
3. Biodegradability and Non-Toxicity
By replacing oil-based materials with plant-based alternatives, which are sourced sustainably and have a lower environmental footprint, we can continue to create significant change towards healthier and safer consumer goods. The impact of renewable plant-based materials on the environment is far less compared to toxic oil-derived counterparts.
Bio-based materials often boast biodegradable properties, mitigating concerns about environmental pollution and waste accumulation. Moreover, by eliminating toxic elements present in conventional materials, such as tin-based catalysts, companies can enhance product safety and reduce environmental harm.
4. Cost Efficiency and Scalability
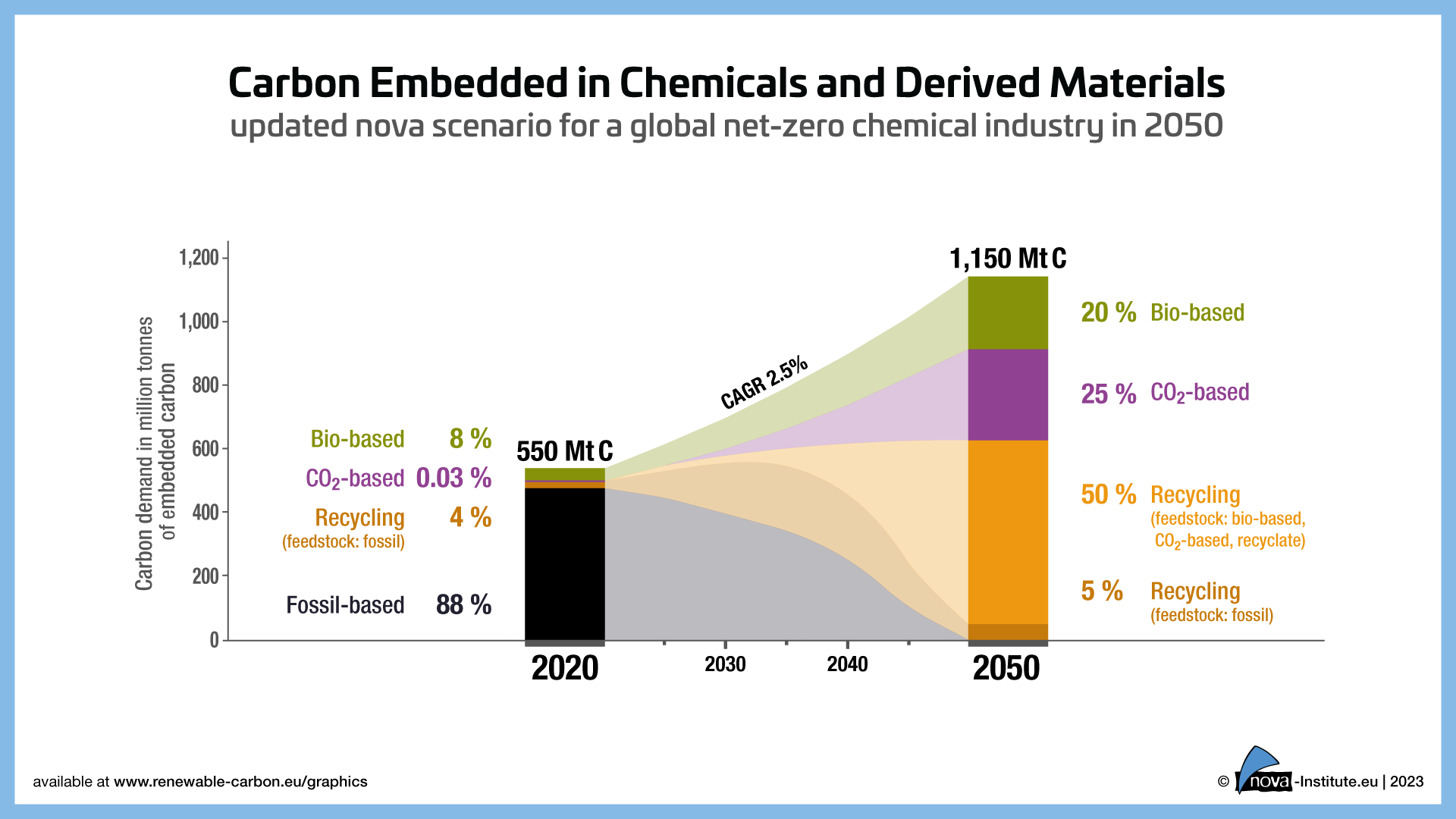
Plants are one of the most abundant renewable resources on earth. Nature produces more plant matter in one day than the sum of all the petrochemistry-based materials produced globally per year. Plant-based chemistry is comparable to petrochemicals without the negative impact, plants have emerged as a sustainable alternative such as coconut husk, ground stone fruit pits, corn, sugarcane, or lignin.
Embracing bio-based materials can be a financially prudent decision for businesses. Not only are these materials becoming increasingly cost-competitive, but they are also designed for scalability, allowing companies to implement sustainable practices without sacrificing profitability.
5. Innovation and Diversification
The adoption of bio-based materials opens doors to innovation and diversification across industries. From textiles and foams to plastics and adhesives, bio-based alternatives offer versatile solutions that cater to a wide range of applications, fostering creativity and driving progress towards a greener future.
The importance of implementing diversified effective mechanisms to decarbonize the global economy and address climate change is crucially important. While internationally there have been societal mechanisms that aim to reduce carbon emissions, such as carbon pricing through carbon taxes or cap and trade systems, there is no one-size-fits-all solution. Further work is needed to achieve our collective goal of reaching net-zero emissions and creating a sustainable future.
Looking Ahead
As we look to the future, the momentum behind defossilization and the adoption of bio-based materials is poised to accelerate. However, this transition requires collective action and commitment from businesses, policymakers, and consumers alike. By divesting from fossil fuel-dependent practices and embracing sustainable alternatives, we can usher in a new era of responsible production and consumption, where environmental stewardship takes precedence. Ultimately, the shift towards bio-based materials is not just a choice but a necessity—one that will shape the sustainability landscape for generations to come.
“By divesting from fossil fuel-dependent practices and embracing sustainable alternatives, we can usher in a new era of responsible production and consumption”
Jason Robinson
We need to believe in the importance of implementing effective mechanisms to defossilize the global material value chain. Our collective goal should be to accelerate the transition away from fossil-derived chemistry by delivering high-performing plant-based alternatives, with quantifiable decarbonization and detoxification benefits.
Materials account for up to 40% of the industry’s GHG emissions, making their impact on the environment undeniable. By defossilizing the supply chain, we can eliminate oil-based raw materials and replace them with plant-based alternatives. This transition not only reduces the carbon footprint but also contributes to a more circular and sustainable economy.