How Circular Economies Are Driving Climate-Smart Agriculture
The circular economy offers a transformative approach for sustainable agriculture, reducing waste, lowering emissions, and improving resource efficiency. Michael Riedijk, Founder & CEO at Lucent BioSciences, discusses how innovations like bio-based fertilizers and regenerative practices enhance resilience, while policy and investment support accelerate this vital transition across industries.
The global agri-food system is at a critical crossroads. Historically seen as a significant greenhouse gas contributor, agriculture is now being reimagined as a key player in combating climate change. Transitioning to climate-smart agriculture requires innovative strategies, and the circular economy stands out as a transformative model. By integrating circular economy principles into agriculture, we can enhance sustainability, improve resource efficiency, and shift toward a low-carbon agri-food system.
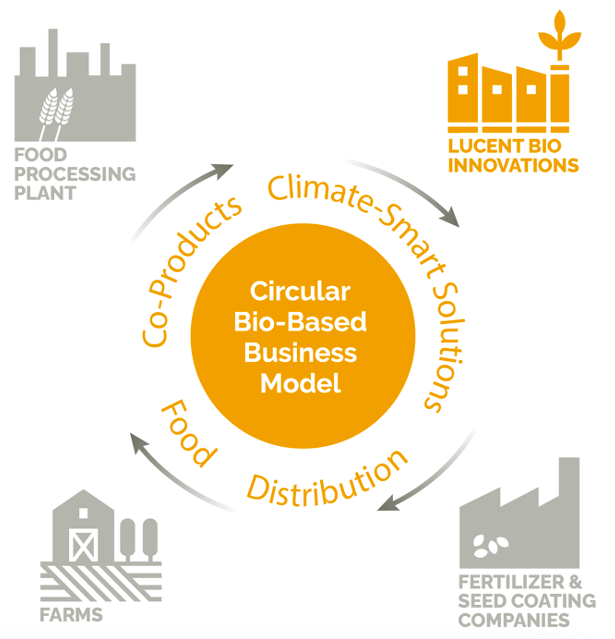
A circular economy, unlike the conventional linear model—where resources are extracted, used and discarded—aims to extend the life cycle of resources. This approach minimizes waste, regenerates natural systems, and closes production loops. In agriculture, this means practices like recycling crop residues, repurposing byproducts, and prioritizing renewable inputs—practices that reduce environmental impact and enhance resilience.
One notable example of circular economy innovation in agriculture is the development of bio-based fertilizers. Soileos micronutrient fertilizers, for instance, are made from up-cycled agricultural residues and supply essential nutrients like zinc and iron to depleted soils. This process transforms low value by-products into high value resources, reduces reliance on synthetic inputs, and aligns with broader sustainability goals. The carbon footprint of these fertilizers is notably lower than traditional chemical alternatives making them an attractive choice for climate-conscious growers.
Circular Practices and Greenhouse Gas Reduction
Beyond nutrient management, circular practices contribute to reducing greenhouse gas emissions. Conventional fertilizers, particularly those containing synthetic nitrogen, contribute significantly to nitrous oxide emissions. In contrast, bio-based solutions have the potential to lower emissions per acre while preserving soil health. This dual benefit is becoming increasingly vital as the sector faces mounting pressure to decarbonize in response to tightening climate policies. Additionally, improved soil health enhances carbon sequestration, increasing the soil’s capacity to store carbon, retain water and nutrients, and better withstand the growing impacts of climate change.
Extending Circular Economy Principles Beyond Agriculture
While the agricultural sector has been a fertile ground for circular economy applications, the concept extends far beyond the farm gate. In the energy sector, circular models are gaining traction, particularly in the recovery and reuse of critical materials from batteries and other end-of-life products. By designing systems with circularity in mind, companies can reduce raw material extraction, lower costs, and improve sustainability outcomes—all of which are essential for industries committed to ambitious climate targets.
Similarly, the manufacturing sector is increasingly prioritizing reuse, refurbishment and recycling. Many companies now design products to be disassembled and recycled at the end of their life cycles. This ensures that valuable resources are reclaimed and reintroduced into the production process, preventing them from becoming waste. The Agtech sector, in particular, can learn valuable lessons from these industries. Integrating circular economy principles into product design and business models can reduce environmental impacts and build resilience into their supply chains, making it a competitive advantage in a rapidly changing market.
“By designing systems with circularity in mind, companies can reduce raw material extraction, lower costs, and improve sustainability outcomes”
-Michael Riedijk
How Policy and Investment Can Accelerate Circular Economies
Accelerating the transition to a circular economy—whether in agriculture or other sectors—requires strategic policy support and targeted investments. Governments play a pivotal role in shaping this landscape through incentives, regulations and funding for innovation. Effective policy tools might include carbon pricing mechanisms that reward lower-emission practices, subsidies that promote regenerative farming, and public investment in research that drives advancements in circular technologies.

Private sector investment is equally crucial. Venture capital and corporate investments can rapidly scale circular innovations, making them accessible to broader markets. Agtech companies have the opportunity to lead by example, developing products and business models that demonstrate the benefits of circularity. This leadership not only meets regulatory and consumer demands but also positions companies at the forefront of a rapidly evolving marketplace.
Building a Climate-Smart Future Through Circularity
The shift toward a circular economy is not just about reducing waste—it’s about fundamentally rethinking how we design, produce, and use resources. For Agtech and sustainability professionals, the benefits are clear: a transition to circular systems supports resilient supply chains, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and meets the growing demand for sustainable food production. These factors are increasingly important as the sector aims to meet global targets while maintaining economic competitiveness.
The agricultural industry’s success with circular principles offers a model that other sectors can follow. Collaboration, knowledge sharing and joint ventures between companies and across industries will be essential for scaling these solutions. By looking at agriculture’s experience with regenerative practices and resource recycling, industries like manufacturing, energy, and construction, can adapt circular approaches to their own unique challenges.
“Collaboration, knowledge sharing and joint ventures between companies and across industries will be essential for scaling these solutions”
-Michael Riedijk
Transforming Agriculture Through Circular Economies
The challenges facing the agriculture sector are immense, but so are the opportunities for transformation. By embracing circular economy principles, we can reshape food production, resource management, and climate change mitigation. A circular approach in agriculture not only reduces emissions and drives regenerative practices but also strengthens the resilience and efficiency of global Agri-food systems.
The momentum is building. As the Agricultural sector moves toward more sustainable practices, circular economy-based innovations will be central to ensuring it can meet the food, fiber and fuel needs of a growing global population while reducing its environmental footprint. The work being done today, from bio-based fertilizers to regenerative farming techniques, is paving the way for a future that balances the demands of productivity with the necessity of sustainability.
Circular solutions are key to this transformation, offering a roadmap to a climate-smart, sustainable future that other industries can adapt and follow. By acting now, businesses across sectors can unlock the potential of circular economies and position themselves as leaders in the global push for decarbonization.